
Use Artificial Intelligence (AI) Performance Routing to instantly accelerate your fleet’s decarbonisation trajectory, and decrease fuel costs. Performance Routing will make a major, quantifiable impact on your fleet’s fuel consumption and CII today, high–impact results from day one.
“DeepSea Vessel Voyage Optimisation AI Solution reduces emissions, it reduces fuel consumption, and it increases safety during operation. It is a win-win in all aspects of sailing“
Geir Fagerheim (SVP Marine Operations) Wallenius Wilhelmsen

Vessel Voyage Optimisation for Decarbonisation – AI Solution:
DeepSea harnesses the latest in AI technology to make ships more efficient. Bringing together experts from technology and maritime, DeepSea focuses on increasing the efficiency and decreasing the fuel consumption of vessels through a combination of technical and operational insights powered by detailed AI-generated performance models. Performance vessel routing for the 21st-century.
We work with forward-thinking shipping companies to make the shipping industry leaner, greener and better connected.

DeepSea works with forward-thinking marine shipping companies to make the maritime shipping industry leaner, greener and better connected. Was founded in 2017 to bring the best of Artificial Intelligence (AI) to the shipping industry and its the shipping’s foremost AI team, powered by the most advanced AI team in the industry. With a culture of active research, contributes academic papers to conferences globally, run international initiatives in AI, and brings all these advancements to its efficiency-boosting products.
DeepSea – AI for the shipping industry
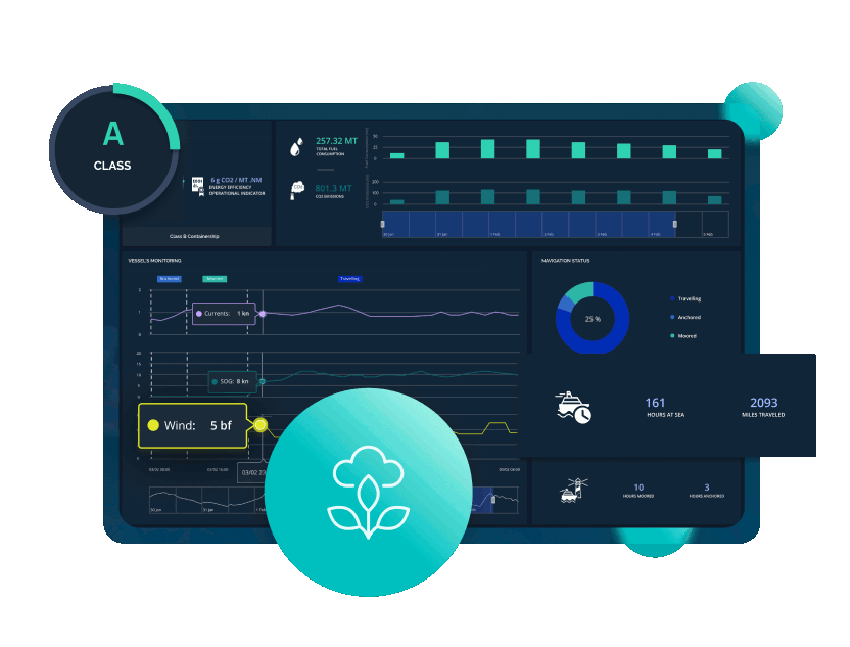
In order to constantly provide an AI driven optimised vessel voyage DeepSea takes data from your vessel and (with AI) creates an accurate vessel model in the Cloud, which is updated, live, to exactly match your vessel’s state and help you run more efficient vessels and more efficient voyages, custom-planned voyages for each vessel.
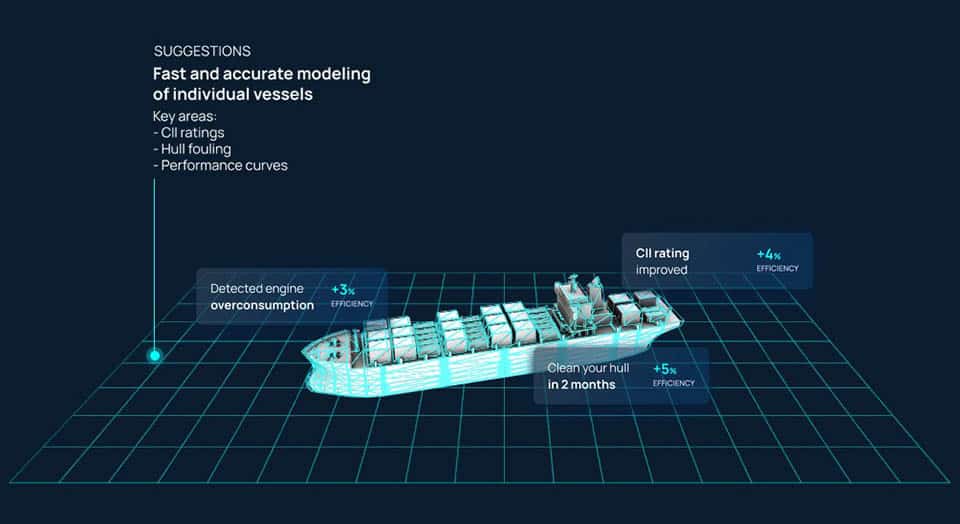
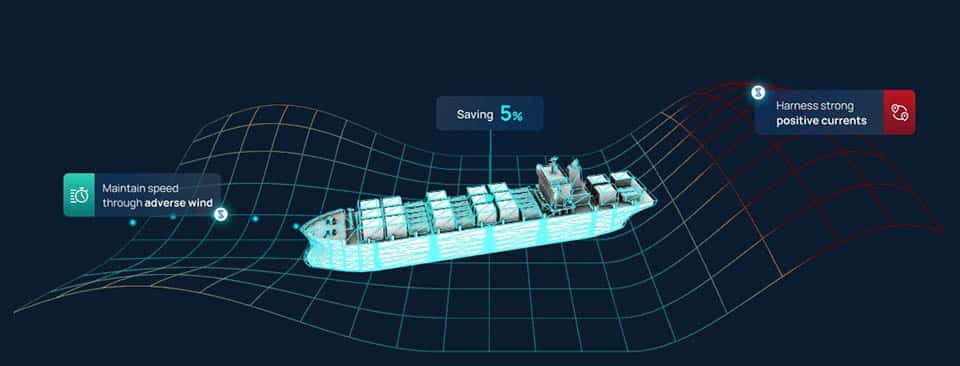
DEEPSEA Pythia – Performance vessel routing for the 21st-century
The world’s first weather routing platform tailored to the exact performance of your vessel, under all weather conditions. Powerful AI models understand exactly how your vessel performs under any weather and fouling conditions.

DeepSea’s platform, is now in place in more than 20 vessel fleets and accurately provides personalized speed and vessel route recommendations for each ship, based on deep learning models trained to predict each ship’s energy consumption in every possible condition.
“No human, no matter how many years of experience they have, can compete with these automated instructions. They reduce emissions, reduce fuel consumption and increase operational safety.”
“It’s a win-win in all aspects of shipping.”
Geir Fagerheim, SVP Marine Operations at Wallenius Wilhelmsen Shipping Company
Wallenius Wilhelmsen, known as a leader in the introduction of new technology and practices in the maritime industry, becomes the first global shipping company to adopt a fully AI-based approach to optimizing ship voyages across its entire fleet of more than 120 Ro-Ro ships.
Wallenius Wilhelmsen, the world’s largest car carrier, conducted a rigorous 18-month trial of DeepSea’s software to reach this deal. “This is a watershed moment for the meaningful and proven implementation of artificial intelligence (AI) in shipping,” said DeepSea President Roberto Cuestas (DeepSea), “There are now many solutions on the market that claim to save fuel, reduce emissions and meet environmental regulations – and most of them are just lip service. It is difficult for shipping companies to distinguish between what is real and what is just marketing. This partnership is another stamp of approval for our technology and approach, from one of the most advanced companies in the industry.” The 18-month trial yielded a fully validated performance improvement of 7% in a subset of Wallenius Wilhelmsen’s fleet, and when the project is completed across the entire fleet, this figure is expected to increase to 10%. This equates to more than 75.000 tonnes of fuel saved and 240.000 tonnes of carbon dioxide (C02) not emitted – and will dramatically help ships comply with new industry emissions regulations. Wallenius Wilhelmsen has set ambitious targets to reduce emissions by 27,5% by 2030. “Half of this reduction should come from existing ships. We are working diligently to find environmentally friendly solutions for our existing fleet. Our goal is to implement this innovative voyage optimization solution for increased vessel efficiency across our entire fleet,” said Geir Fagerheim, SVP Marine Operations at Wallenius Wilhelmsen.
– – –
The clients of the Greek company DeepSea AI, which include shipping companies from Singapore, Norway, Japan, etc., can save, through DeepSea’s technology, 8%-12% in fuel and reduce their environmental footprint. The way for the development of autonomous ships, where their route is “determined” not by the ship captain but by an algorithm, is opened by the acquisition of DeepSea Technologies founded by Konstantinos Kyriakopoulos and Roberto Kousta, by the Japanese multinational Nabtesco, listed on the stock exchange Tokyo.
“The technology we have been developing for so many years was heading in this direction. Now we have the right partner, which allows us to realize this goal, as we did not have a hardware system. With the combination of our technologies, we can also convert existing ships into autonomous ones, as well as install our systems on new ships,” says Mr. Kyriakopoulos, speaking about the goal of the acquisition of DeepSea by Nabtesco. DeepSea has developed an artificial intelligence platform which, through the collection – in real time – of data concerning the performance of commercial ships (tankers, containers) during navigation, creates models to optimize their performance (fuel saving, reduction carbon emissions) taking into account the weather conditions, the characteristics of the respective ship, etc.
Its technology is used on over 300 ships. “Essentially with this artificial intelligence model we help the captain reach his destination with the least possible environmental pollution and the best possible performance”, explains Mr. Koustas. This is where DeepSea and Nabtesco’s systems ‘merge’ together in which will be able to automate the ‘commands’ given to the ship by DeepSea (eg the optimal speed of the ship based on the weather conditions). “The ship’s autonomy will be based on the best possible control of its every movement to save even more fuel,” says Mr. Kyriakopoulos.
According to the company, its customers, which include shipping companies from Singapore, Norway, Japan, etc., can use DeepSea’s technology to save 8%-12% in fuel and reduce their environmental footprint. The latter is considered crucial, as the imposition of a carbon tax on shipping is being discussed, with European Union exerting pressure on the shipping sector.
DeepSea’s team, which consists of 90 people – 80% are located in Greece – is expected to increase to 110 in the next period, while Athens is being transformed into an artificial intelligence center for the Japanese company’s activities. These are not limited to the shipping industry, but extend to railway automation, aviation, wind turbines, etc. “With Nabtesco’s investment, technologies around what we call industrial artificial intelligence (industrial AI) will be developed in Greece,” says Mr. Kyriakopoulos. “We have a long-term action plan to implement what we want in autonomy and artificial intelligence”.
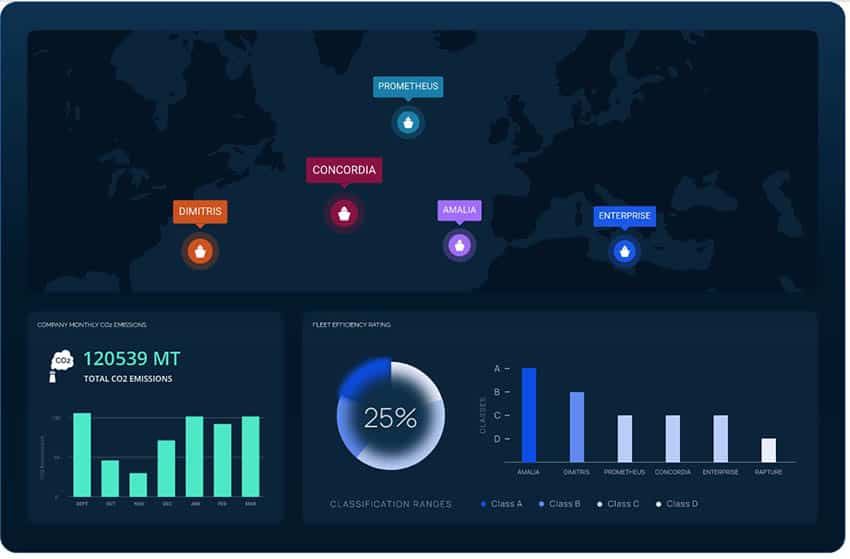
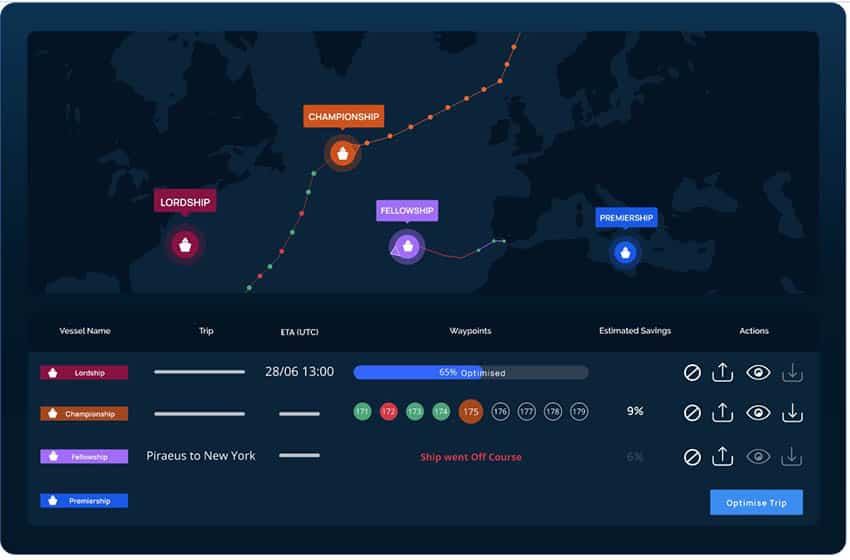
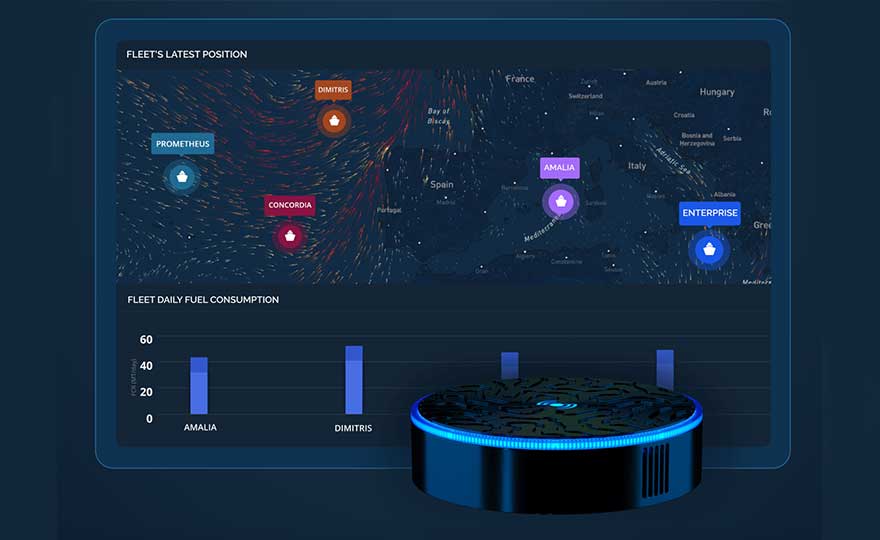
(September 7th, 2022) Wallenius Wilhelmsen became the first global shipping company to adopt a fully AI-based approach to voyage optimisation across its entire fleet of 120+ ships.
Wallenius Wilhelmsen shipping company rolled out DeepSea’s Performance Routing software, which provides vessel-specific route and speed plans, in the final quarter of 2022 and 2023. One of the most forward-thinking companies in the industry of maritime shipping, Wallenius Wilhelmsen has set ambitious targets to reduce emission by 27,5 per cent by 2030. This work with DeepSea is an important step towards meeting them.
Geir Fagerheim, SVP Marine Operations at Wallenius Wilhelmsen, says:
“No human being, no matter how many years of experience they have, can compete with these automated sailing instructions. It reduces emissions, it reduces fuel consumption, and it increases safety during operation. It is a win-win in all aspects of sailing.”
This landmark decision, the first of its kind globally, was not made quickly – but followed 18 months of rigorous step-by-step testing.
The numbers that ultimately came out of this comprehensive trial period are significant:
A 6,9% improvement in vessel efficiency and more than 170.000 tonne predicted reduction in emissions across the fleet.
However, equally important to focus on are the key learnings that emerged from the 18-month period of intense collaboration that led to this partnership.
On 13th October, Wallenius Wilhelmsen and DeepSea performed a virtual webinar discussing online this validation period and together discussed their key learnings for decarbonisation with vessel voyage optimisation (Voyage Optimisation for Decarbonisation – online webinar).

What is the 10% initiative? A movement to reduce maritime vessel energy costs by 10%, the approach is proven, cost-effective and can be achieved within 12 months. The 10% initiative is a commitment by DeepSea and the members (EUROSEAS Ltd, EuroDRY Ltd, ETF Partners, Nabtesco) of the initiative to work collaboratively to do something real, measurable, and impactful – with tangible benefits for everyone.
When it comes to voyage optimisation – picking the best course and speed for the journey – the ships’ captains don’t have the tools to make informed decisions, explains Mr Fagerheim of shipping company Wallenius Wilhelmsen (cargo ships). This is why they go hard and fast at the start of the journey, because they can’t predict later conditions. This is where AI-powered voyage optimisation platforms comes in.
The adoption of AI solutions in the maritime industry is at a nascent stage, however, Artificial Intelligence has an immense potential to unlock value in optimizing fleet efficiency. AI technology for voyage optimisation is primarily focused on reducing vessel fuel consumption, resulting in the reduction of CO2 emissions and running costs. Lloyd’s Register’s Maritime Performance Services has developed vast experience is in the use of AI for vessel optimisation and helping to ultimately improve vessel performance. Traditional and legacy data analytics only look at 10% of vessel data, whereas AI models can now look at close to 100% of vessel data and process this data instantaneously to create extremely accurate vessel performance insights around fuel consumption, speed, trim, hull fouling and power consumption,” (Andy McKeran, Director of Maritime Performance Services, Lloyd’s Register). Spend on AI Artificial Intelligence solutions in the maritime shipping industry is expected to more than double in the next five years to $2,7 billion by 2027, a compound annual growth rate of 23%.
Machine learning: The next maritime frontier?
As the availability of data for high performance computing is increasing alongside the adoption of automation, Wärtsilä Voyage believes that artificial intelligence and machine learning are technologies to keep an eye on.
Four ways in which Maritime Industry is investing in AI for performance management
AI, IOT, Business Intelligence, Data Analytics are changing the way shipping operates, and also cutting costs and reducing risk to human lives. Leading shipping companies have deployed AI-assisted technologies to gain greater insight into their ships’ performance, while both established companies and start-ups are finding new ways to push the boundaries of AI.
Artificial Intelligence and the Era of Autonomous Shipping
The world is interconnected through global trade on the basis of a transportation industry. And, it will continue to grow, with a predicted rise of nearly a third in seaborne-trade towards 2030, and with increases in tonne-mileage up to 74,000 billion over the forecast period.
In other words, the ocean will experience substantial increases in traffic, pressure will get much higher and risk of marine accidents and incidents at sea will persist. It is estimated that roughly 90% of marine casualties and incidents caused by human mistakes, costing over EUR1.4 billion in marine liability insurance claims.
This in fact has urged businesses to invest in automation underpinned by transformational technologies of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning, as the ultimate solution to improve productivity, efficiency and safety by eliminating human errors.
Statistics have shown that AI has the capability to boost the transportation and logistics industry performance by almost 90%, potentially increase the industry’s annual revenue up to EUR0.45 trillion.
“Autonomous shipping is the future of the maritime industry. As disruptive as the smartphone, the smart ship will revolutionise the landscape of ship design and operations”
Mikael Mäkinen, President, Marine at Rolls-Royce Plc.
The maritime shipping sector has been working hard to find ways to decrease carbon fuel emissions inline with the Initial IMO GHG Strategy and the Maritime 2050 agenda with a heavy focus on autonomy and future fuels. But as pressure continues to grow in the wake of COP26 solutions which unlock the potential for a reduction across existing vessel fleets are imperative.
A brief introduction to AI (Artificial Intelligence) and its applications in the maritime industry
During the 2023 SMART4SEA Athens Forum, Mr Themistoklis Sardis, (IT Manager at Costamare Shipping Company S.A.) explained that there are several AI applications in the shipping industry, including automation of cargo handling and management, optimization of routes and logistics, and predictive maintenance of ships and other equipment.
While many industries benefit from and use AI to streamline operations and receive valuable insights, each has unique applications. Understanding how the maritime industry is adapting AI and machine learning can better prepare you for working on the water alongside this equipment
Free Buyers Guide – Leading artificial intelligence (AI) companies for the shipping industry
A free document (buyers guide) that includes detailed information on the Shipping AI solutions manufacturers and suppliers and their vessel routing optimisation and planning products, along with contact details, to inform your purchasing decision (download a free copy).
Shipping 4.0 : The Future of the Maritime Industry
Steam. Electricity. Internet. These three industrial revolutions, changed everything about the way the world works. Today, we’re in the middle of the fourth industrial revolution: Artificial intelligence (AI). Contrary to the common belief that shipping operates in a traditional, “old-fashioned” model, new strides as part of this automation-driven industrial revolution have created new patterns of innovation and change. This is Shipping 4.0.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)? Artificial intelligence leverages computers and machines to mimic the problem-solving and decision-making capabilities of the human mind. (IBM)
Artificial intelligence is the intelligence of machines or software, as opposed to the intelligence of human beings or animals. (Artificial Intelligence – Wikipedia)
Artificial intelligence, the ability of a computer or computer-controlled robot to perform tasks commonly associated with intelligent beings. (Artificial intelligence (AI): Definition, Examples, Types – Britannica)
What is artificial intelligence (AI)?
Artificial intelligence is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems. Specific applications of AI include expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition and machine vision.
How does AI work?
As the hype around AI has accelerated, vendors have been scrambling to promote how their products and services use it. Often, what they refer to as AI is simply a component of the technology, such as machine learning. AI requires a foundation of specialized hardware and software for writing and training machine learning algorithms. No single programming language is synonymous with AI, but Python, R, Java, C++ and Julia have features popular with AI developers. (What is Artificial Intelligence and How Does AI Work – TechTarget)
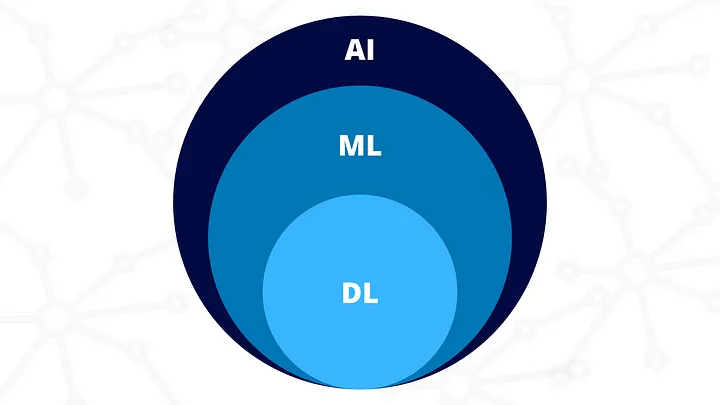
Differences between AI, Machine Learning and Deep Learning
AI, machine learning and deep learning are common terms in enterprise IT and sometimes used interchangeably, especially by companies in their marketing materials. But there are distinctions (see more at: AI vs. machine learning vs. deep learning: Key differences (techtarget.com)
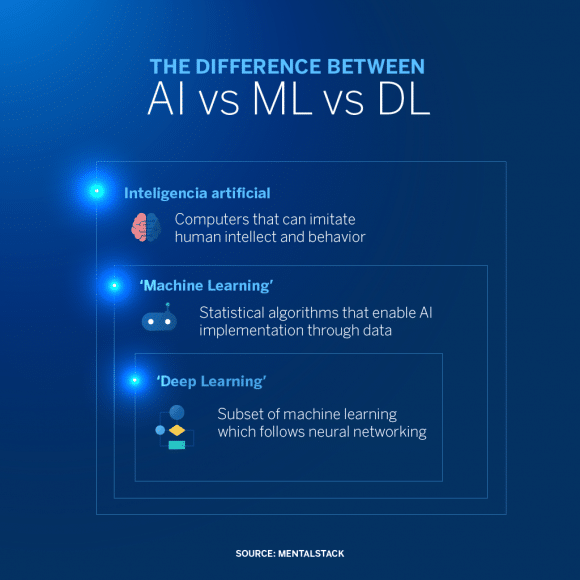
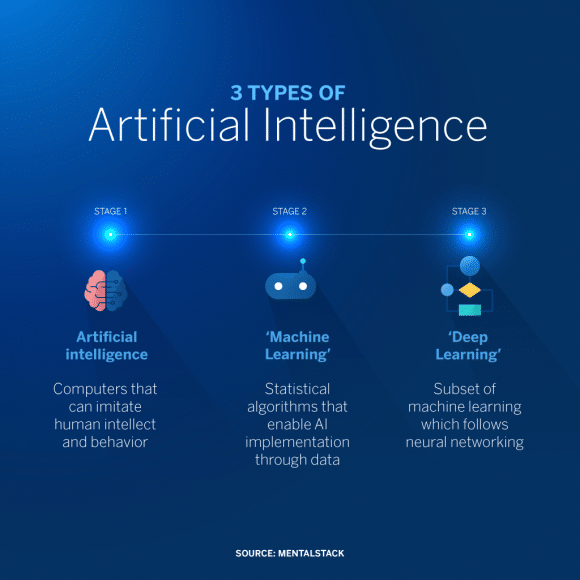
What are the 4 types of AI intelligence?
Some of these types of AI aren’t even scientifically possible right now. According to the current system of classification, there are four primary AI types: reactive, limited memory, theory of mind, and self-aware. (Source: Understanding the 4 Types of Artificial intelligence – bernardmarr.com )
What Is AI? Learn About Artificial Intelligence – a very comprehensive article on AI, by Oracle.com
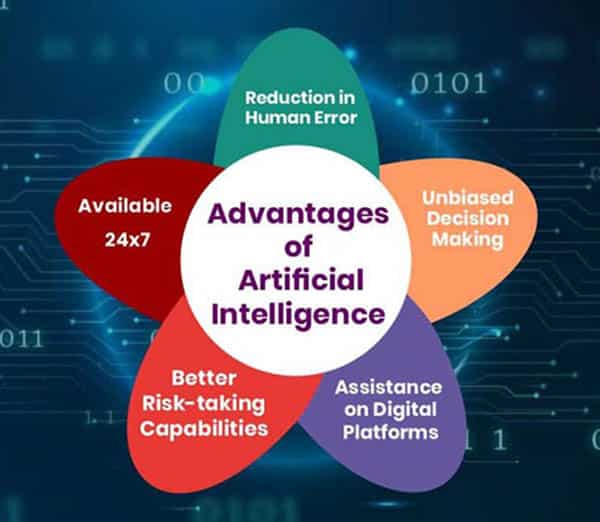
Advantages and Disadvantages on the use of Artificial Intelligence
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)? (according to an AI app itself 🙂 … ChatGPT)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks include things like learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, language understanding, and even decision-making.
AI systems are designed to analyze data, recognize patterns, and make informed decisions or predictions based on that data. They can be trained to improve their performance over time through iterative learning processes. AI technologies are broadly classified into two categories: Narrow or Weak AI and General or Strong AI.
Narrow or Weak AI: This type of AI is designed and trained for a specific task or a narrow range of tasks. It excels at performing those tasks, often surpassing human capabilities, but it lacks the ability to understand or perform tasks outside of its predefined scope. Examples of narrow AI include voice assistants like Siri or Alexa, image recognition systems, and recommendation algorithms used by streaming services.
General or Strong AI: General AI refers to a level of artificial intelligence that has the ability to understand, learn, and apply knowledge across a wide variety of tasks, much like a human being. It would possess human-like cognitive abilities and could potentially perform any intellectual task that a human can. General AI remains largely theoretical at this point and has not been achieved.
AI systems can be further categorized into machine learning and deep learning:
Machine Learning: It is a subset of AI that involves training algorithms to learn patterns from data and make predictions or decisions based on that data. Types of machine learning include supervised learning (training with labeled data), unsupervised learning (finding patterns in unlabeled data), and reinforcement learning (learning through trial and error).
Deep Learning: This is a subset of machine learning that utilizes artificial neural networks to model and process complex patterns and relationships in data. Deep learning has been particularly successful in tasks like image and speech recognition.
AI has a wide range of applications across various industries, including healthcare, finance, transportation, entertainment, and more. It continues to advance rapidly and has the potential to revolutionize how we live and work, although ethical considerations and potential challenges also need to be carefully addressed as AI technology progresses.



Find all top providers of Marine Navigation products & services for safe Maritime Voyage Planning