Cables, pipelines, roads, sea straits, air routes and satellites form the fragile network on which the global economy is built. These are invisible networks of enormous importance to the global supply chain and modern life, which, however, are only remembered when a war like the one in Ukraine or Israel threatens one of these strategic points. Deutsche Bank study sheds light on the five weak links of the global economy. That is, the infrastructures that cannot be replaced by some alternative and therefore, can block the global supply chain.
There are some vulnerabilities in the global economy that are more or less known to everyone, such as Taiwan’s semiconductor factories, global financial centers and the 0.5% of subway stations in London and Paris that could block the half network.
But there are also the invisible but very important networks, as was shown by the damage done to an undersea gas pipeline and telecommunications cable between Finland and Estonia on October 10, reminiscent of the sabotage of the Nord Stream pipeline a year ago. In 2010, the eruption of a volcano in Iceland “grounded” one second of Europe’s air traffic for 8 days, notes Deutsche Bank.
Both Ukraine and Israel are located near such important points for the global economy.
– Data cables: Up to 99% of the world’s digital communications as well as 10 trillion financial transactions. dollars, pass through fiber optic cables located on the sea floor. There are approximately 550 active and planned cables, spanning 1.4 million kilometres. Many are barely thicker than a watering can, explains Deutsche Bank. These cables are vulnerable to espionage and sabotage and to accidental damage.
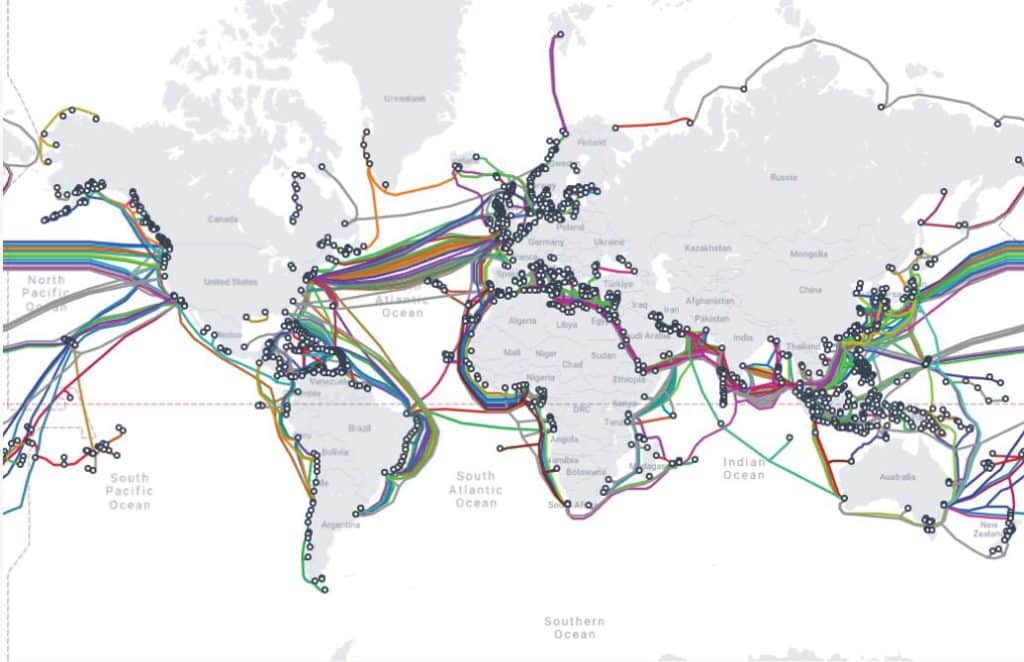
– Undersea power cables: Power interconnectors allow countries to buy cheaper wind or solar power from their neighbors with more favorable weather, increasing security of supply and better managing demand. But, they can be destroyed by sabotage or accident.
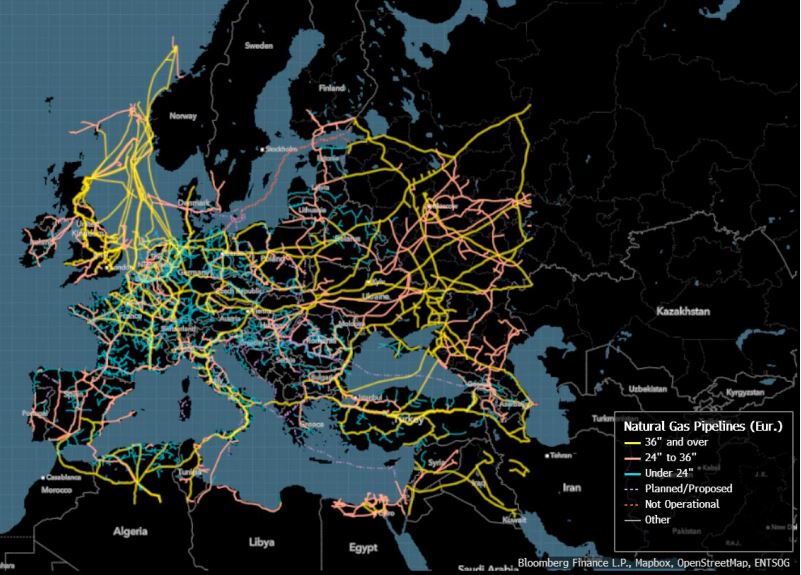
– Natural gas pipelines: Europe depends on pipelines for most of its natural gas supplies. In 2020 it imported almost 40% of its natural gas from Russia, and since then, it has had to rely on pipelines from Norway and imported LNG. As the Nord Stream explosions showed, these pipelines are vulnerable to sabotage.
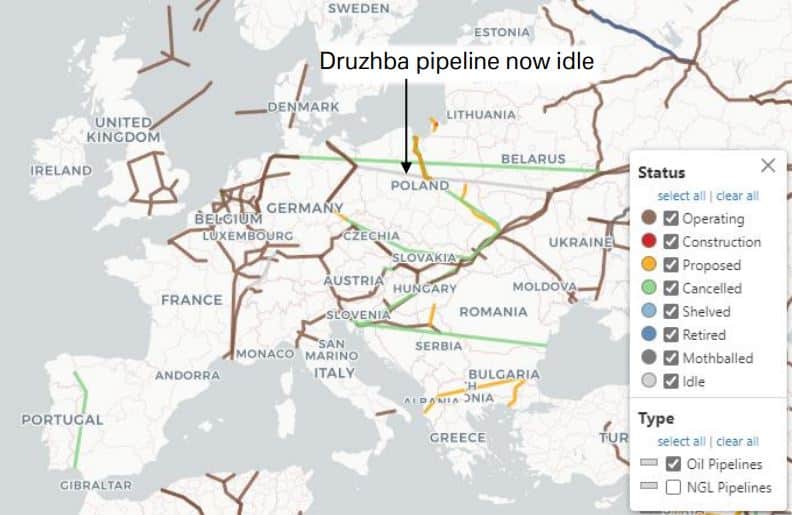
– Oil pipelines: Most of the world’s oil pipelines are located in Europe and Asia and start from Russia. A typical oil pipeline is about 50 centimeters in diameter and can carry over 1 million liters (or 6.300 barrels per hour). By comparison, a barrel can carry less than 200 barrels at a time. Pipelines are made of steel and, where possible, are buried in the ground. Like natural gas pipelines, they are vulnerable to damage, earthquakes and sabotage.
Some railways and roads in far-flung places carry a disproportionately large share of supplies critical to the global economy, with no alternatives. A vast area in the Congo and Zambia, for example, is Africa’s largest producer of copper and accounts for two-thirds of the world’s cobalt production. But there are only four roads, all bad and congested, to transport these raw materials from the mines to ports in Namibia, South Africa, Mozambique and Tanzania. Something similar is happening with Brazil’s soy, which is the world’s No. 1 exporter. In the last two years, drought has hit rivers that are vital waterways, showing how vulnerable these transports are.
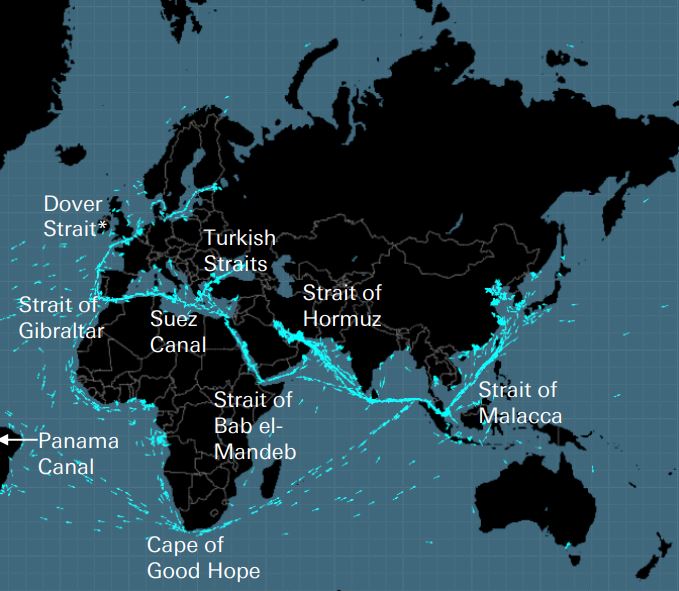
Along with the Cape of Good Hope, there are 8 important “straits” for sea transport. As Deutsche Bank explains, these are the five “keys that unlocked the world” for the British Empire, if the Straits of Dover are removed and the Panama Canal, the Turkish Straits, the Straits of Bab el Madeb and the Straits of Hormuz are added . In oil, for example, more than 60% of supply is transported by sea, with the Straits of Hormuz being the most important point for the market, since a fifth of the world’s consumption (and a third of LNG) passes through it. At its narrowest point, the Straits of Hormuz are only 33 kilometers wide.

These straits are vulnerable to blockades, ship collisions or groundings, pirates, terrorist attacks, wars and accidents such as oil spills.
Air transport depends on an invisible network of corridors that can be disrupted by weather, wars or unusual events, such as when Spain’s airspace was closed last November to allow a Chinese missile to enter Earth’s atmosphere. Strikes by air traffic controllers have caused major transport problems in Europe this year, while the biggest post-war air traffic blockade occurred in 2010, when the volcano in Iceland erupted.
The world is very dependent on the US Global Positioning System (GPS). This uses approximately 30 Earth-orbiting Positioning, Navigation and Timing (PNT) satellites, which send signals to over 4 billion users worldwide. But these signals are weak and prone to interference, and it has been estimated that if GPS is “cut”, the cost will exceed $1 billion a day, just for the US.
(SOURCE: https://www.moneyreview.gr/business-and-finance/125480/deutsche-bank-ta-aorata-diktya-poy-kinoyn-tin-pagkosmia-oikonomia-oi-5-adynamoi-krikoi/)



Find all top providers of Marine Navigation products & services for safe Maritime Voyage Planning