Kabel, jaringan pipa, jalan raya, selat laut, jalur udara dan satelit membentuk jaringan rapuh yang menjadi landasan perekonomian global. Ini adalah jaringan tak terlihat yang sangat penting bagi rantai pasokan global dan kehidupan modern, namun hanya diingat ketika perang seperti yang terjadi di Ukraina atau Israel mengancam salah satu titik strategis tersebut. Studi Deutsche Bank menyoroti lima mata rantai lemah dalam perekonomian global. Artinya, infrastruktur yang tidak dapat digantikan oleh alternatif lain sehingga dapat menghambat rantai pasokan global.
Ada beberapa kerentanan dalam perekonomian global yang kurang lebih diketahui semua orang, seperti pabrik semikonduktor Taiwan, pusat keuangan global, dan stasiun kereta bawah tanah 0,5% di London dan Paris yang dapat memblokir separuh jaringan.
Namun ada juga jaringan yang tidak terlihat namun sangat penting, seperti yang ditunjukkan oleh kerusakan yang terjadi pada pipa gas bawah laut dan kabel telekomunikasi antara Finlandia dan Estonia pada tanggal 10 Oktober, yang mengingatkan kita pada sabotase pipa Nord Stream setahun yang lalu. Pada tahun 2010, letusan gunung berapi di Islandia “menghentikan” satu detik lalu lintas udara Eropa selama 8 hari, catat Deutsche Bank.
Baik Ukraina maupun Israel terletak dekat dengan titik-titik penting bagi perekonomian global.
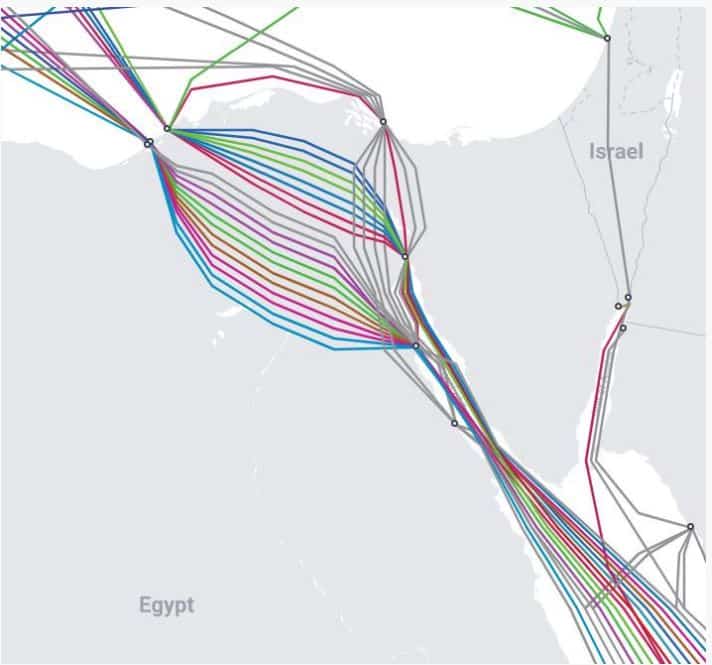
– Kabel data: Hingga 99% komunikasi digital dunia serta 10 triliun transaksi keuangan. dolar, melewati kabel serat optik yang terletak di dasar laut. Terdapat sekitar 550 kabel aktif dan terencana, yang membentang sepanjang 1,4 juta kilometer. Banyak yang tidak lebih tebal dari kaleng penyiram, jelas Deutsche Bank. Kabel ini rentan terhadap spionase dan sabotase serta kerusakan yang tidak disengaja.
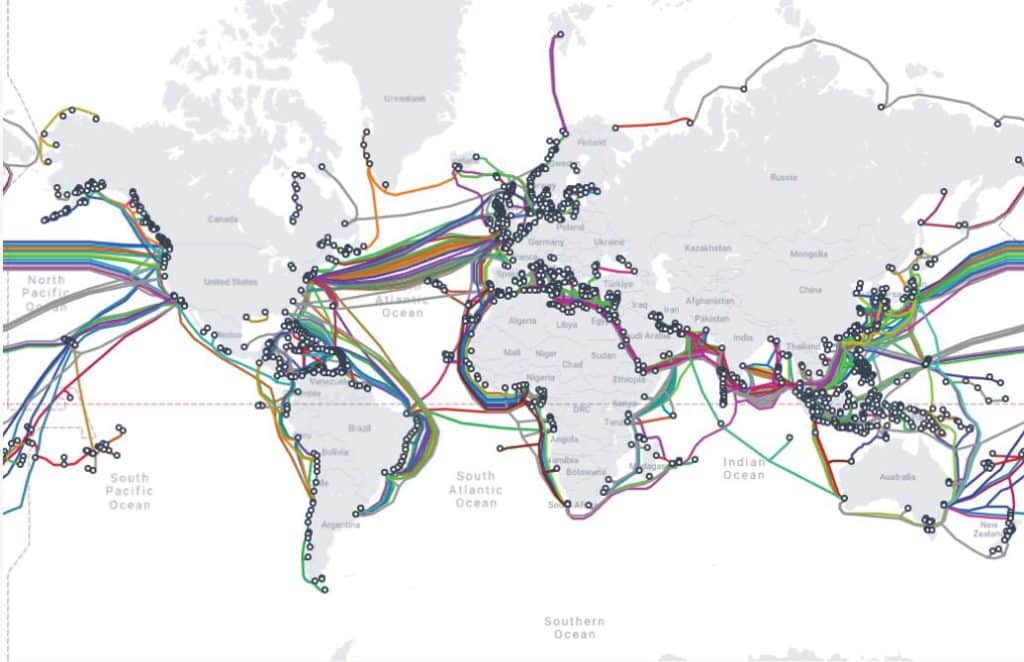
– Kabel listrik bawah laut: Interkonektor listrik memungkinkan negara-negara membeli tenaga angin atau surya yang lebih murah dari negara-negara tetangga mereka yang memiliki cuaca lebih baik, meningkatkan keamanan pasokan, dan mengelola permintaan dengan lebih baik. Namun, mereka dapat dihancurkan karena sabotase atau kecelakaan.
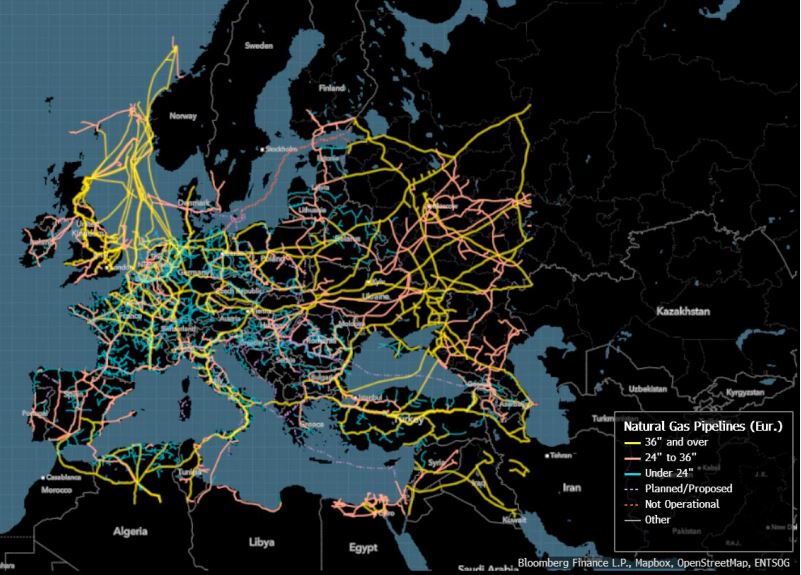
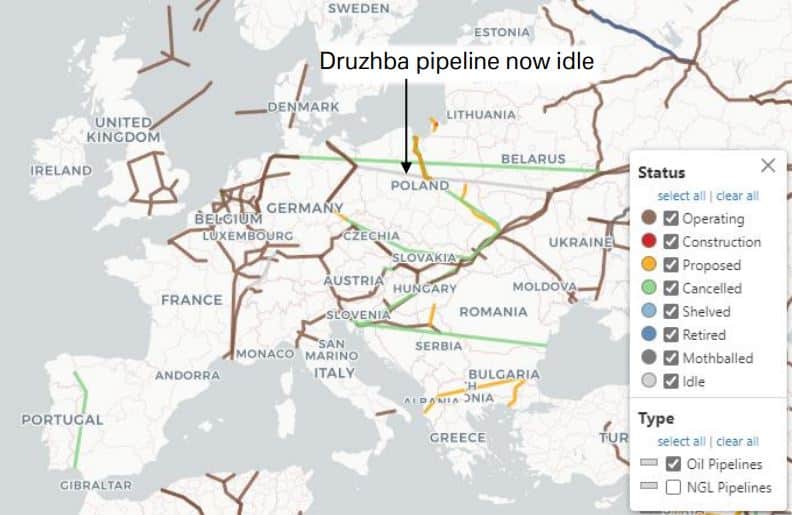
– Jaringan pipa gas alam: Eropa bergantung pada jaringan pipa untuk sebagian besar pasokan gas alamnya. Pada tahun 2020, mereka mengimpor hampir 40% gas alamnya dari Rusia, dan sejak itu, mereka harus bergantung pada jaringan pipa dari Norwegia dan mengimpor LNG. Seperti yang ditunjukkan oleh ledakan di Nord Stream, jaringan pipa ini rentan terhadap sabotase.
– Saluran pipa minyak: Sebagian besar jaringan pipa minyak dunia berlokasi di Eropa dan Asia dan dimulai dari Rusia. Pipa minyak pada umumnya berdiameter sekitar 50 sentimeter dan dapat mengalirkan lebih dari 1 juta liter (atau 6.300 barel per jam). Sebagai perbandingan, satu barel bisa membawa kurang dari 200 barel sekaligus. Saluran pipa terbuat dari baja dan, jika memungkinkan, dikubur di dalam tanah. Seperti jaringan pipa gas alam, jaringan pipa ini rentan terhadap kerusakan, gempa bumi, dan sabotase.
Beberapa jalur kereta api dan jalan raya di tempat yang berjauhan membawa pasokan yang sangat penting bagi perekonomian global dalam jumlah yang sangat besar, sehingga tidak ada alternatif lain. Misalnya, wilayah yang luas di Kongo dan Zambia merupakan penghasil tembaga terbesar di Afrika dan menyumbang dua pertiga produksi kobalt dunia. Namun hanya ada empat jalan, semuanya rusak dan padat, untuk mengangkut bahan mentah ini dari tambang ke pelabuhan di Namibia, Afrika Selatan, Mozambik, dan Tanzania. Hal serupa juga terjadi pada kedelai Brasil, yang merupakan eksportir nomor satu di dunia. Dalam dua tahun terakhir, kekeringan telah melanda sungai-sungai yang merupakan saluran air penting, yang menunjukkan betapa rentannya transportasi tersebut.
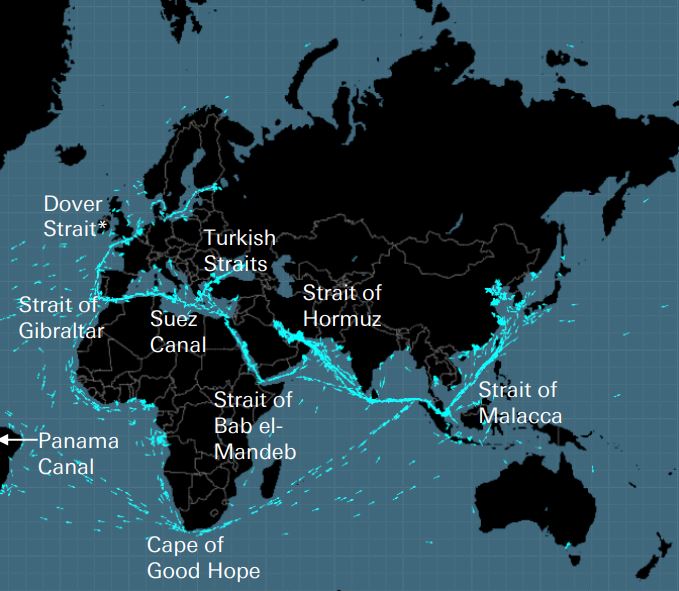
Selain Tanjung Harapan, terdapat 8 “selat” penting untuk transportasi laut. Seperti yang dijelaskan Deutsche Bank, inilah lima “kunci yang membuka dunia” bagi Kerajaan Inggris, jika Selat Dover dihilangkan dan Terusan Panama, Selat Turki, Selat Bab el Madeb, dan Selat Hormuz ditambahkan. . Misalnya saja pada minyak bumi, lebih dari 60% pasokannya diangkut melalui laut, dengan Selat Hormuz menjadi titik terpenting bagi pasar, karena seperlima konsumsi dunia (dan sepertiga LNG) melewati selat tersebut. Pada titik tersempitnya, Selat Hormuz hanya selebar 33 kilometer.

Selat-selat ini rentan terhadap blokade, tabrakan atau kandasnya kapal, bajak laut, serangan teroris, perang dan kecelakaan seperti tumpahan minyak.
Transportasi udara bergantung pada jaringan koridor tak kasat mata yang dapat terganggu oleh cuaca, perang, atau kejadian tidak biasa, seperti ketika wilayah udara Spanyol ditutup pada November lalu untuk memungkinkan rudal Tiongkok memasuki atmosfer bumi. Pemogokan yang dilakukan oleh pengawas lalu lintas udara telah menyebabkan masalah transportasi besar di Eropa tahun ini, sementara blokade lalu lintas udara terbesar pasca perang terjadi pada tahun 2010, ketika gunung berapi di Islandia meletus.
Dunia sangat bergantung pada Global Positioning System (GPS) AS. Ini menggunakan sekitar 30 satelit Positioning, Navigation and Timing (PNT) yang mengorbit Bumi, yang mengirimkan sinyal ke lebih dari 4 miliar pengguna di seluruh dunia. Namun sinyal-sinyal ini lemah dan rentan terhadap gangguan, dan diperkirakan jika GPS “dipotong”, biayanya akan melebihi $1 miliar per hari, hanya untuk AS.
(SUMBER: https://www.moneyreview.gr/business-and-finance/125480/deutsche-bank-ta-aorata-diktya-poy-kinoyn-tin-pagkosmia-oikonomia-oi-5-adynamoi-krikoi/)



Temukan semua penyedia produk & layanan Navigasi Laut teratas untuk Perencanaan Pelayaran Maritim yang aman